Background: Machine learning applied to medical imaging labor under a lack of trust due to the inscrutability of AI models and the lack of explanations for their outcomes. Explainable AI has therefore become an essential research topic. Unfortunately, many AI models, both research and commercial, are unavailable for white-box examination, in which access to a model’s internals is required. There is therefore a need for black-box explainability tools in the medical domain. Several such tools for general images exist, but their relative strengths and weak- nesses when applied to medical images have not been explored.
Methods: We use a publicly available dataset of brain MRI images and a model trained to classify cancerous and non-cancerous slices to assess a number of black-box explainability tools (LIME, RISE, IG, SHAP and ReX) and one white-box tool (Grad-CAM) as a baseline comparator. We use several common measures to assess the con- condance of the explanations with clinician provided annotations, including the Dice Coefficient, Hausdorff Distance, Jaccard Index and propose a Penalised Dice Coefficient which combines the strengths of these measures.
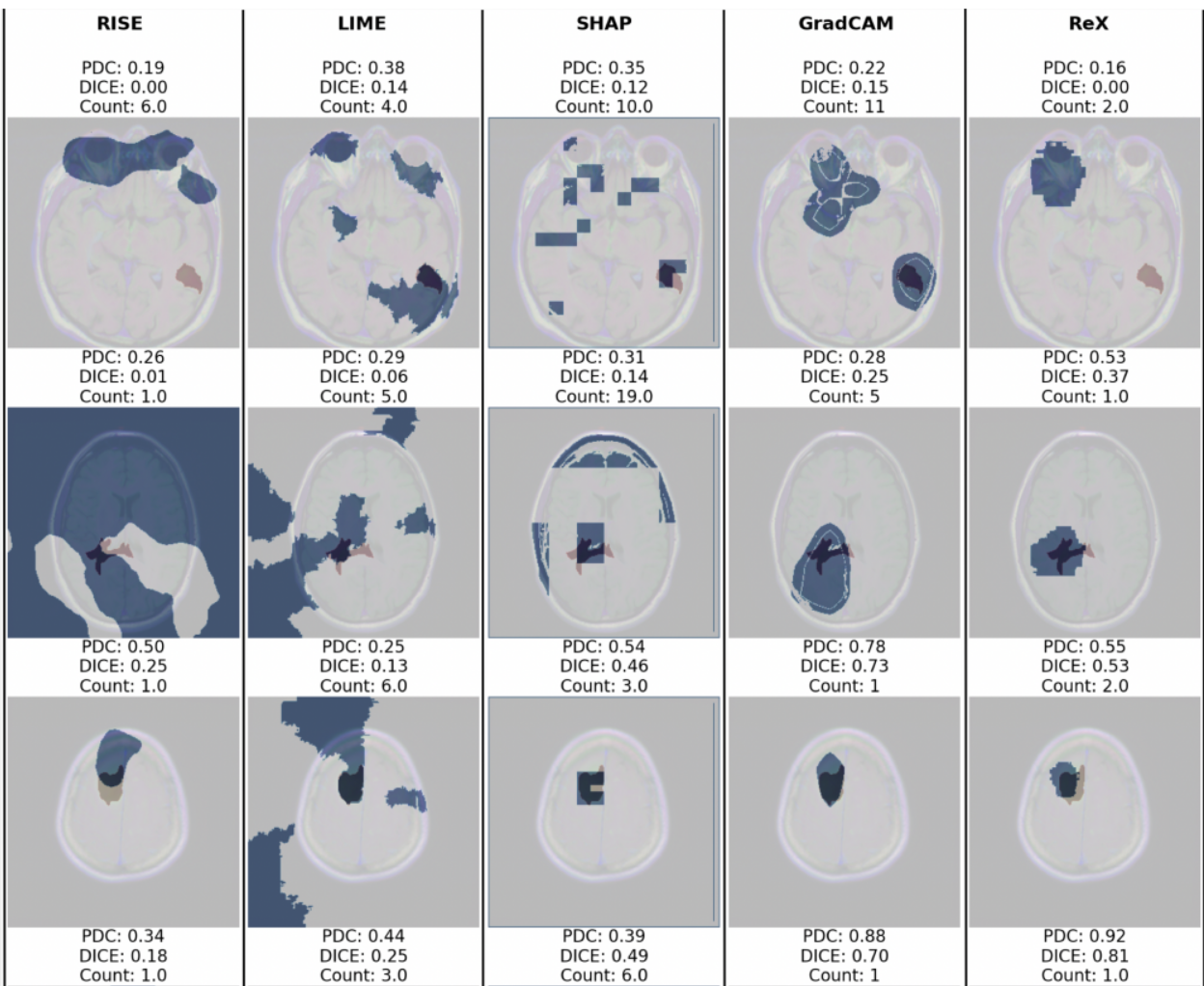
Results: ReX (Dice Coefficient = 0.42±0.20) consistently performs relatively well across all measures with comparable performance to Grad-CAM (Dice Coef- ficient = 0.33±0.22). A panel of images is presented for qualitative inspection, showing a number of failure modes.
Conclusion: In contrast to general images, we find evidence that most black-box explainability tools do not perform well for medical image classifications when used with default settings.